
The owner’s capital would include all owner contributions to a business. Revenues would include items such as retail sales and similar gross income line items. Expenses could be items such as the cost of goods sold, administrative expenses, and payroll. The accounting equation is ingeniously designed to always remain balanced, meaning the total amount of assets will always equal the sum of liabilities and equity. For instance, when a company takes out a loan, assets (cash) increase, as do liabilities (loans payable), which keeps the equation balanced.

Example of the Expanded Accounting Equation
- A company’s balance sheet is the source of its accounting equation numbers.
- Service Revenues is an operating revenue account and will appear at the beginning of the company’s income statement.
- We could also use the expanded accounting equation to see the effect of reinvested earnings ($419,155), other comprehensive income ($18,370), and treasury stock ($225,674).
- Machinery is usually specific to a manufacturing business that has a factory producing goods.
It also tells us that the company has assets of $9,900 and the only claim against those assets is the owner’s claim. It is easy to see that an additional investment by the owner will directly increase the owner’s equity. Similarly, a withdrawal of money by the owner for personal use will decrease the amount of owner’s equity. The first step to do so is to learn how to identify and analyse business events or transactions. Then it will be a matter of identifying the accounting components and recording the transaction. Examples of supplies (office supplies) include pens, paper, and pencils.

Accounting Equation for a Corporation: Transactions C5–C6

Equity increases from revenues and owner investments accounting equation expanded (stock issuances) and decreases from expenses and dividends. These equity relationships are conveyed by expanding the accounting equation to include debits and credits in double-entry form. The dividend could be paid with cash or be a distribution of more company stock to current shareholders. An account is a contra account if its normal balance is opposite of the normal balance of the category to which it belongs.
The Surprisingly Fast Way to Become Financially Independent (5 Powerful Levers)
- Equity is also affected by issuing new shares or repurchasing existing ones, which can alter stockholder value and market perception.
- Since the business has not yet provided the product or service, it cannot recognise the customer’s payment as revenue, according to the revenue recognition principle.
- The expanded accounting equation allows accountants to identify the impact on the owner’s equity in detail.
- By including these additional components, the expanded accounting equation provides a more detailed view of a company’s financial position and performance.
- The difference between the revenue and profit generated and expenses and losses incurred reflects the effect of net income (NI) on stockholders’ equity.
For example net sales is gross sales minus the sales returns, the sales Online Bookkeeping allowances, and the sales discounts. The net realizable value of the accounts receivable is the accounts receivable minus the allowance for doubtful accounts. Assets are resources owned by a company that are expected to provide future economic benefits. They are categorized as current, like cash, accounts receivable, and inventory, or non-current, such as property, plant, and equipment. Assets are recorded on the balance sheet at historical cost, following Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP).
Equity is also influenced by market conditions and investor sentiment. Stock buybacks, for example, reduce outstanding shares, potentially boosting earnings per share (EPS) and signaling confidence in the company’s financial health. Monitoring equity trends is essential for understanding how internal and external factors shape a company’s financial position. Explore the expanded accounting equation, its components, and how it provides a detailed view of financial transactions and equity changes. Since corporations, partnerships, and sole proprietorships are different types of entities, they have different types of owners.
- This essential yet powerful tool will act as your compass, pointing you in the right direction when assessing your business’s financial health.
- This is useful for outside analysts, who base their stock recommendations on detailed analyses of this type.
- The totals indicate that as of midnight on December 7, the company had assets of $17,200 and the sources were $7,120 from the creditors and $10,080 from the owner of the company.
- The totals also reveal that the company had assets of $17,200 and the creditors had a claim of $7,000.
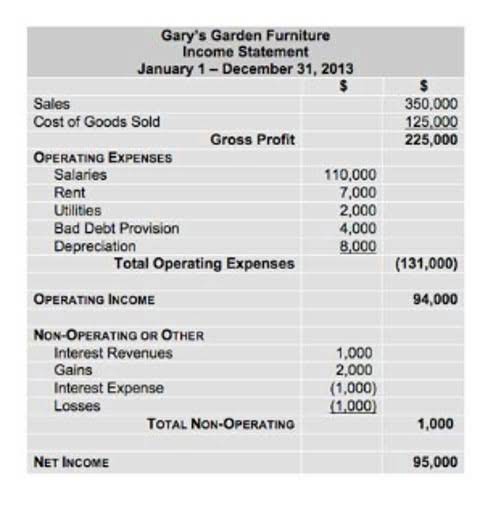
Let’s look at an example of the “expanded” accounting equation so we can better understand the concept. Beginning retained earnings refers to the earnings that have been kept by the company at the beginning of the accounting period compared to the previous period. Once again, the equation stays balanced because the decrease in cash is offset by the decrease in equity through the owner’s withdrawals. A balanced accounting equation starts with an efficient AP process. Gain control, reduce errors, and improve financial accuracy with expert strategies. In the following tutorial, we’ll look at some adjusting entries problems of recording transactions to get some practice at using the full accounting equation.


Comentários